No Certs. No Service.
We hate greenwashing too. We are proud of the research, testing and certifications done to create the drinking straw that can change the world.

The use of PHAs for foodservice applications is a new innovation but the highly biodegradable properties of PHA are well known and have been studied by the scientific community for well over a decade.
The development of phade® involved a rigorous testing and certification process performed by numerous independent labs and third-party certification bodies. When examining any products claiming to be green, sustainable, or eco-friendly, look for these gold standards in testing. We proudly display our certifications, so that when we say that phade® is working better for the planet, you know we have the stats to prove it.

The result: phade® passed the standard requirement (at least 90% biodegradation within six months) in these conditions.

The result: phade® met the standard requirement (at least 90% biodegradation within six months) in these conditions.
Industrial compostability is determined by ASTM D6400 Standard Specification for Labeling of Plastics Designed to be Aerobically Composted in Municipal or Industrial Facilities, which is a pass/fail standard. To pass ASTM D6400, the product must:
BPI has certified our phade® straw as industrially compostable because it has passed ASTM D6400.
TUV Austria – has also certified our phade® straw as industrial compostable using the same ASTM D6400 pass/fail test and certification requirements as BPI.
The results: phade® exceeded the standard requirements for certification. Using ISO 14855, phade® biodegraded at least 90% in 90 days (the standard being within one year), and using ISO20200, phade® achieved 100% disintegration within 61 days (the standard being at least 90% of test material reduced to less than 2mm after 26 weeks). phade® passed TUV’s safety requirements for toxicity.

TUV Austria has developed a home compostable certification and has certified our phade straw as home compostable.
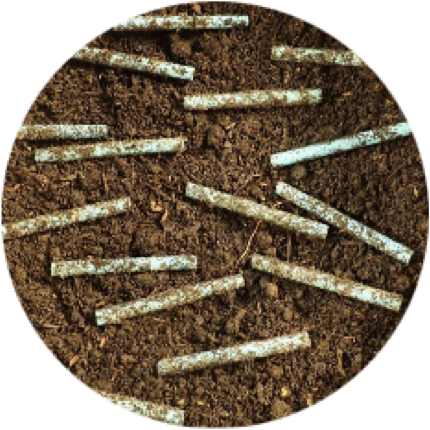
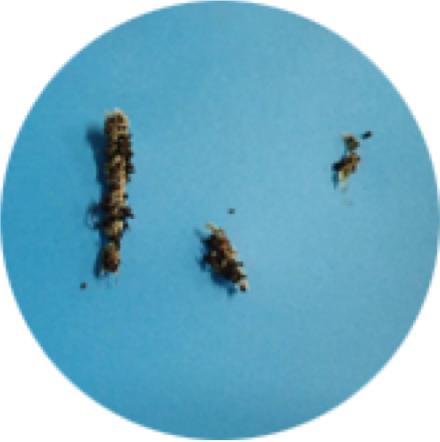



ASTM – D6691
The result: met the standard requirement (90% biodegradation in 180 days) in just 98 days. Residual Water Raman Spectroscopy: Complete biodegradation, no microplastics. Residual Water NMR Spectroscopy: Complete biodegradation, no microplastics.
ASTM D6691– Standard Test Method for Determining Aerobic Biodegradation of Plastic Materials in the Marine Environment by a Defined Microbial Consortium or Natural Sea Water Inoculum
Testing conducted at University of Georgia Lab (Raman Spectroscopy) and Danimer Scientific Laboratory, Athens, GA (NMR Spectroscopy).